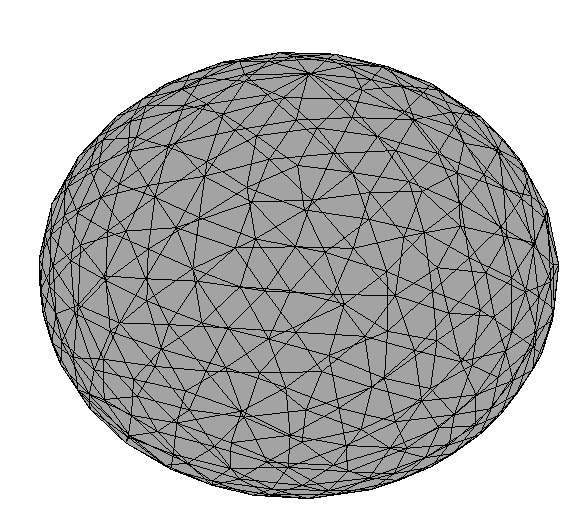
Create an Mesh Object
You can create a Mesh object by
mesh = Mesh(v4e, x); % 1D line mesh / v4e: 2 x nrE
mesh = Mesh(v4e, x, y); % 2D triangular mesh / v4e: 3 x nrE
mesh = Mesh(v4e, x, y, z); % 3D tetrahedral mesh / v4e: 4 x nrEwhere v4e(:,i) contains vertex index for each element.
Or, you can get uniform mesh by
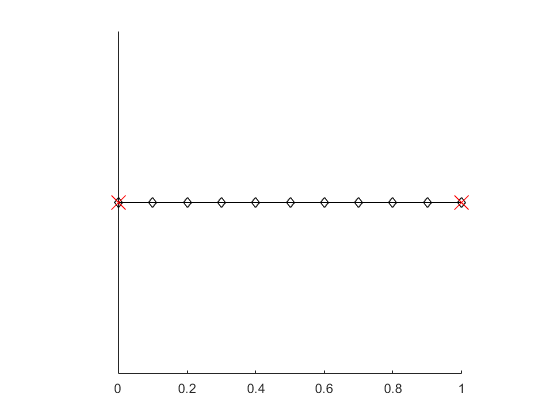
% 1D uniform mesh in (0,1) with 10 elements.
mesh = line2linemesh(0,1,10);
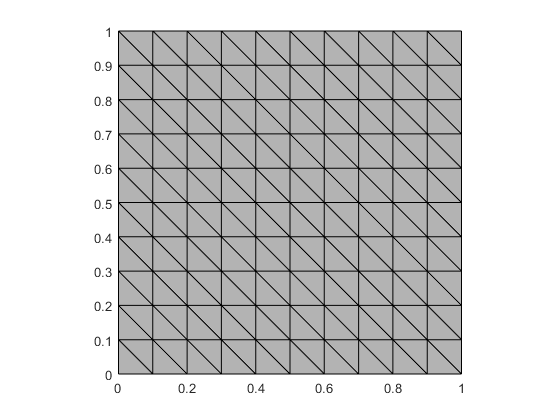
% 2D uniform mesh in (0,1)x(0,2) with 10 x 20 (x2) elements.
mesh = rect2rectmesh(0,1,0,2,10,20);
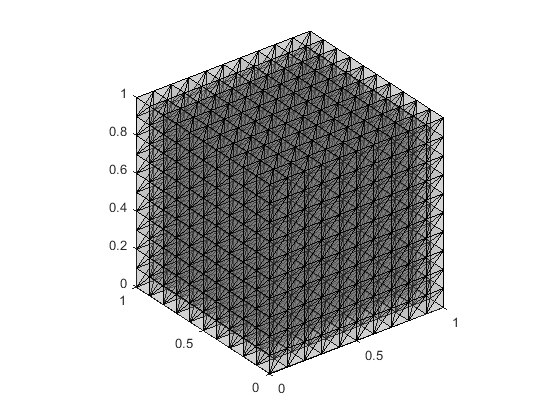
% 3D uniform mesh in (0,1)x(0,2)x(0,3) with 10 x 20 x 30 (x6) elements
mesh = cube2cubemesh(0,1,0,2,0,3,10,20,30);Display Mesh
To show the mesh, you can use show() method.
mesh.show(); % default configuration
mesh.show('FaceColor', 'r'); % change face color
mesh.show(ax, __); % specify target axeswhere the optional arguments are from plot for 1D and patch for 2D and
3D
Facet Information
When a Mesh object is created, facet information can be obtained, where
v4fis the vertex index for each facetx4fis the x-coordinate for each facet (or y, z)nx4fis the facet normal for each facet (or y, z)J4fis the Jacobian for each facete4fis the neighboring elements' index for each facetef4fis the neighboring elements' local facet index for each facetfmaskandfmask_negare the local facet vertex index of an element (positive / negative)
All information about facets can be obtained seperately for interior/boundary facets
by changing f to f0 or fb.
If you want to access to the first neighboring element to 10th facet, you can use
mesh.e4f(1,10); % gives the first neighboring element of 10th facet
mesh.ef4f(1,10); % gives the positive element's which facet is 10th facet.In other words,
mesh.v4f(:,10) == mesh.v4e(mesh.fmask(:,mesh.ef4f(1,10)), mesh.e4f(1,10))Or, for negative element (the second neighboring element)
mesh.v4f(:,10) == mesh.v4e(mesh.fmask_neg(:,mesh.ef4f(2,10)), mesh.e4f(2,10))Note that e4fb and ef4fb are 1 x nrfb vectors
since there is only one neighboring element.
mesh = rect2trimesh(); % get uniform triangular mesh
figure;
mesh.show(); % display mesh
hold on;
plot(mesh.x4fb, mesh.y4fb, 'r', 'linewidth', 2); % plot boundary edges
plot(mesh.x4f0, mesh.y4f0, 'b', 'linewidth', 1.5); % plot interior edges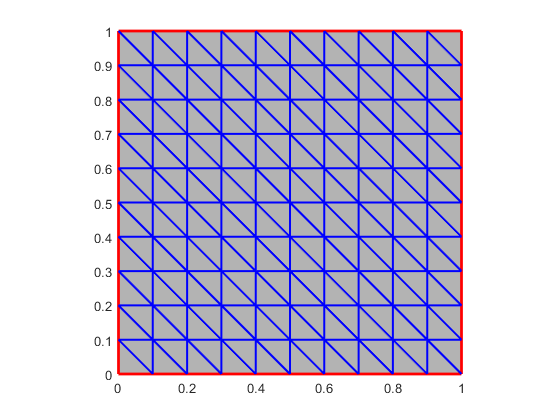
Affine Information
In finite element assembly, affine information of physical triangles is often used.
One can access to the affine information by
% dX/dR
mesh.xr, mesh.xs, mesh.xm
mesh.yr, mesh.ys, mesh.ym
mesh.zr, mesh.zs, mesh.zm
% Jacobial
mesh.J
% dR/dX
mesh.rx, mesh.ry, mesh.rz
mesh.sx, mesh.sy, mesh.sz
mesh.mx, mesh.my, mesh.mzHere, each property is 1 x nrE vector.